Symptoms of a Bad Brake Booster
The brake booster is the heart of the dynamic braking system. When you press the brake pedal, the booster multiplies the force on your foot, reducing the force required to stop. When a brake booster fails, you may notice it immediately because the problem usually produces one or more obvious symptoms. Knowing the symptoms of a malfunctioning brake booster can save you from a traffic accident or expensive car repairs. So what are the signs of a bad brake booster?
What is a Brake Booster?
As mentioned earlier, a brake booster reduces the amount of force the driver needs to apply the brakes. The booster does this by applying force to the master cylinder, a device that distributes pressurized fluid to actuate the brakes.
There are three main types of brake boosters:
- Vacuum-operated
- Hydro-boost
- Electronic assemblies
Vacuum Operated Brake Booster
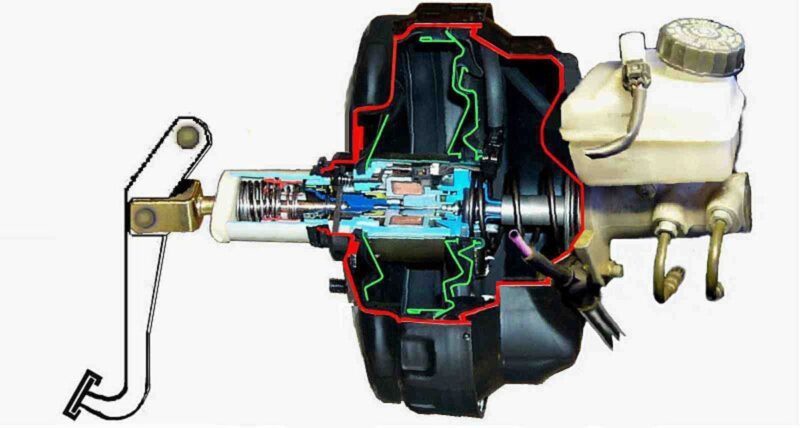
Most brake boosters are vacuum operated. With this design, the inner diaphragm separates the two sides of the booster. The sides are sometimes called vacuum chambers and working chambers.
When the brake is released, the vacuum in both chambers is equal. Depressing the brake pedal operates the control valve, allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the working chamber. As a result, a pressure differential is created that causes the pushrod of the booster to apply force to the master cylinder, creating brake assist.
Hydro-boost booster
Some vehicles use hydraulically assisted brake boosters. With this type of booster, the power steering pump produces hydraulic pressure to provide brake assist. The pressure from the pump acts on the power piston within the hydraulic booster assembly. The piston then pushes the output rod, which applies force to the master cylinder.
Electronic assemblies
Electronic brake booster assemblies are becoming more common. This design is typically suitable for hybrid and electric vehicles with zero (or limited) engine vacuum and electric power steering.
There are several electronic brake booster designs in use today. Each uses a set of sensors (ie, pedal travel sensors, speed sensors, etc.) to determine the operating conditions of the vehicle. The electronic control unit (ECU) uses this information to activate the electronic brake booster.
The booster and master cylinder then generate the hydraulic pressure needed to provide brake assist.
Usually, the electronic brake booster is integrated with the master cylinder and ECU in one assembly. Other components may also be part of the assembly.
The Important Role of the Brake Booster

The brake booster plays an important role in braking a car equipped with disc brakes. The unit sits under the hood and provides extra force to the brakes and helps stop. Without it, stopping distances would increase significantly, exposing drivers and passengers to a greater risk of collision during emergency stops.
Inside the brake booster, two chambers separated by a diaphragm experience a similar drop in pressure as air rushes into the engine through the air intake, creating a vacuum. Depressing the brake pedal opens a valve and air is drawn into one side of the booster. This allows the vacuum present on the other side to pull on the diaphragm. A rod connected to the brake pedal assembly passes through the center of the diaphragm to the master cylinder piston.
When the piston rod transmits the force applied to the brake pedal, the diaphragm also pulls the piston rod and increases the force on the master cylinder piston. The combined force makes the car slow down quickly and easily. Release the brake pedal, the valve closes, and the system returns to balance.
If you recognize the following bad brake booster symptoms, act immediately—don’t ignore them. They indicate that your car has become unsafe.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bad Brake Booster?
The following are symptoms that indicate a damaged brake booster:
1. Hard brake pedal
A common sign of a damaged brake booster is difficulty pressing the hard brake pedal.
When you observe that the brake pedal becomes hard and hard to engage, check your braking system. Driving a car with a hard brake pedal is not a good idea because it becomes unmanageable. You only put yourself at risk of being involved in an accident. You should not drive until the problem is resolved.
2. Long parking time
This is one of the common symptoms of a damaged master cylinder when the brake booster is damaged. When you notice that your car takes longer to come to a complete stop while the brake pedal is still firm, then there is likely a problem with the brake booster. This happens because of the presence of air or any air leaks. Try checking for leaks in the booster hose or if the clamps are tight.
This is a dangerous situation when driving in snail-like traffic. The risk of a traffic accident is high, so you want to know how to test your brake booster once you observe this symptom.
3. The brake pedal is slightly higher than usual
Many people may miss this, especially when they’re not paying attention. Most people can go as long as the brake pedal responds appropriately. However, you should be able to detect if the brake pedal is slightly stronger than normal. The first sign is that your feet will feel weird. If you’re very observant, you may find that whenever you hit the brakes, your pedals are a little stronger than before.
If you find yourself in this situation, then you’d better get your brake booster checked.
4. The engine keeps stalling
Does your engine stall when you hit the brakes? You may not easily attribute this to a faulty brake booster, as constant engine stalling is a symptom of many possible failures in your car. That’s why as soon as you hit the brakes, your car shuts off.
The diaphragm of the brake booster can fail at any time. When this happens, excess air from the engine enters the brakes and bypasses the seals. This can cause the car to stall as soon as the brake pedal is pressed.
Once you notice this, you should check your car as this problem can easily turn into a serious problem. Aside from the possibility of brake failure, if you keep driving the car without fixing the problem, you could damage the transmission.
5. Hissing
One of the symptoms of a damaged brake booster is a hissing sound from the dashboard or under the brake pedal. The reason for the hissing sound is that the vacuum is starting to escape. So whenever you press the brake pedal and the brakes make noises, chances are your brake booster is broken or about to break. Note that if the noise is coming from the engine bay or the area of the brake pedal, this noise could be a symptom of a damaged brake booster.
6. Liquid leakage
This is also one of the symptoms of a damaged brake booster check valve. When you observe a leak in your brake system, especially around the brake pedal, your brake booster may be damaged. This is because hydraulically assisted brake boosters use power steering fluid, and when it leaks, some of the fluid that makes it work effectively is lost in the process.
7. Warning light
A warning light is triggered when the brake booster fails. These lights come on when certain sensors in the braking system detect a malfunction. So, when you see the brake warning light-triggered, it’s a sign that something is wrong with your brakes. Low fluid levels, damaged master cylinders, and other causes can cause these lights to come on.
Conclusion
The brake booster is an important aspect of your car’s braking system, which is why you must know the symptoms of a damaged brake booster. This is because early detection of a bad brake booster will save you the possibility of an accident due to faulty car brakes. When you catch and fix bad supercharger problems early, you can also avoid more complicated problems with your car. Now that you can identify the symptoms of a malfunctioning brake booster, you can save yourself a ton of complications and problems. However, if you have replaced your brake booster and find that the new brake booster is not working, you may want professional help.


Average Rating